Palmer , states that modal auxiliary verbs help language users express 'what should be', 'what may be', 'what would be', and 'what is'. Thus, the authors of the articles make frequent use of modal verbs to show possibility, necessity and prediction in their writing. As the results in the frequency table indicates, the authors of articles on covid-19 use more will to indicate prediction.
Will accounts for 28.9% of the modal auxiliary used and this is the highest percentage. Modality involves the claims or assertions of a person assuming the position of authority and claiming or asserting to have the knowledge of what will happen in future. On this basis the results given the use of modal auxiliarywill indicates what will happen in future. Modal verbs or modal auxiliary verbs are a type of verbs that indicates modality, i.e., likelihood, permission, ability and obligation. Some of the common modal verbs are can, could, may, might and must. Modals cannot be represented alone as a main verb since they are always used in the helping form.
The data was analyzed manually with regard to different functions of the modal auxiliary verbs in question. Six categories of modal auxiliaries namely; Ability, possibility, prediction, obligation, intention and quasi-legal modals characterized the data. Findings indicate that the authors of the articles chose predictive auxiliary modals will, may, can and should in that order in the articles.
Other types of modal used are would, must and might. The modals used presented the opinions of the article writers and the use of will reported the highest frequency. Pro to generate frequency lists and concordance lines.
It was found that the most frequent modal auxiliary verbs used in horoscope are will and may to express prediction and possibility. The least used modal auxiliary verbs are should and must which are modals of necessity and obligation. The pronoun you is the most frequent lexis in every Horoscope entry. Based on findings from this study, Horoscopes can be used to teach the modal auxiliary verbs in addition to prescribed Malaysian text books. This study does not also seek to use modal auxiliary verb for pedagogical purposes but to report on journalists' opinion of Covid-19.
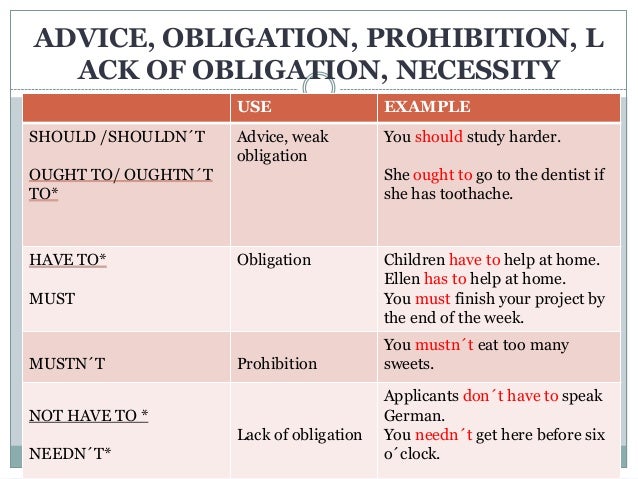
What Are The Two Types Of Modal Verbs Modal verbs that express degrees of necessity range from obligation to no obligation . Obligation or Necessity (100%) The strongest modals of necessity represent a total obligation. Of these verbs, only has to can be used in the past tense. Advice We also use modal verbs to give advice. We can use some of these modals in the past form to lament past decisions.
Expectation Some modals establish expectation or an outside pressure to do something. You are supposed to take off your shoes. They can also establish that expectation in the past.
You were supposed to take off your shoes. Suggestion Other modal verbs provide suggestion, which lacks the strength of obligation/expectation/advice. These can be used to show the suggestion in the past as well. No Obligation or Necessity (0%) Finally, the negative form of have to shows a lack of necessity. This has the same meaning in the past form.
Remember that modal verbs are auxiliary verbs, or helping verbs, that are most commonly used to talk about possibility or necessity. You can also use modal verbs to ask for and give permission, describe ability, and give advice. Al, researched on modal auxiliaries and their semantic functions used by advanced EFL learners. In English, main verbs but not modal verbs always require the auxiliary verb do to form negations and questions, and do can be used with main verbs to form emphatic affirmative statements.
Have to is often grouped with modal auxiliary verbs for convenience, but in fact it is not a modal verb. In the have to structure, "have" is a main verb. Having collected the frequency data, the data was analyzed manually with regard to different functions of the modal auxiliary verbs in question.
Uses of modals in this paper are derived from Quirk et al schema of modal auxiliaries. In the strict sense, though, these other verbs do not qualify as modal verbs in English because they do not allow subject-auxiliary inversion, nor do they allow negation with not. If, however, one defines modal verb entirely in terms of meaning contribution, then these other verbs would also be modals and so the list here would have to be greatly expanded. In the have to structure, "have" is a main verb. There are two types of modal verbs of obligation ; those that primarily express a firm obligation or necessity – must and have to. Those that express a recommendation or moral obligation – should and ought to.
He meaning 'intention' is implied when the circumstances clearly involve a future event that is planned by the speaker. As one of the functions of an article in the newspaper is to inform and report events, the most obvious cases revealed in the corpus show that the writer reports the intention of others. The data used below indicate auxiliary verbs showing intention. This research was designed to analyze modal auxiliary used, their frequency, and the uses of modal auxiliary verbs in Daily Nation Newspaper.
It used a purposive design to select the newspapers articles for the period 1St April to 30thApril 2020. For the purpose of this paper the data was drawn for the period 1stto 10th April as this formed the pilot project for data collection. It is the wider research that will use the data collected for the whole period. In many Germanic languages, the modal verbs may be used in more functions than in English. In German, for instance, modals can occur as non-finite verbs, which means they can be subordinate to other verbs in verb catenae; they need not appear as the clause root. In Swedish, some modal verbs have infinitive forms.
This for instance enables catenae containing several modal auxiliaries. The modal verbs are underlined in the following table. There are two types of modal verbs of obligation ; those that primarily express a firm obligation or necessity - must and have to. Those that express a recommendation or moral obligation - should and ought to.
A modal verb is an auxiliary verb that expresses necessity or possibility. An auxiliary verb, also called a helping verb, "helps" other verbs show moods and tenses. Auxiliary verbs include forms of do, be, and have. It was also not the intention of the paper to undertake a frequency analysis of the various types of functions of the modal auxiliary verbs.
The data of the modals in Daily Nations collected and analyzed show different distribution of frequency in modal auxiliary verbs. Any conclusions or claims are made exclusively on the basis of corpus observations. The corpus for this research was modal auxiliary verbs extracted from Daily Nation newspaper for the period stated above.
Ahmad et al, examined the use of different modal verbs for the purpose of personal stance marking in Pakistani English newspaper editorials. The study suggests that the readers of Pakistani English newspaper editorials should be conscious of the fact that the editorials might be biased and affect their opinion. There is a huge number of studies in modality and this indicates how rich the field is.
In English grammar, a modal is a verb that combines with another verb to indicate mood or tense. A modal, also known as a modal auxiliary or modal verb, expresses necessity, uncertainty, possibility, or permission. It is a normal verb which is used as a modal verb.
It uses the auxiliary verbdo to form the negative and it is followed by a noun phrase orto + base form. Hawaiian Pidgin is a creole language most of whose vocabulary, but not grammar, is drawn from English. As is generally the case with creole languages, it is an isolating language and modality is typically indicated by the use of invariant pre-verbal auxiliaries. The invariance of the modal auxiliaries to person, number, and tense makes them analogous to modal auxiliaries in English.
However, as in most creoles the main verbs are also invariant; the auxiliaries are distinguished by their use in combination with a main verb. -,gamōtmaymögen, magmogen, magmögen, magmeie, meimagmå(må)mega, mámagum, magwissen, weißweten, weet? Witte, witweetvedvetvita, veitwitum, wait(tharf)dürfen, darfdurven, durfdörven, dörvdoarre, doardurf? Þaúrbum, þarfThe English could is the preterite form of can; should is the preterite of shall; might is the preterite of may; and must was originally the preterite form of mote. (This is ignoring the use of "may" as a vestige of the subjunctive mood in English.) These verbs have acquired an independent, present tense meaning.
The German verb möchten is sometimes taught as a vocabulary word and included in the list of modal verbs, but it is actually the past subjunctive form of mögen. Modal verbs help when speaking about ability, making requests and offers, asking permission, and more. The modal auxiliary mayhas been used 28 times in the articles, representing a total of 13.3%. Thus, it occurs quite frequently in the articles. As a modal verb in the articles, may is used to expresses ability.
It is used to express ability in sentences 6 and 7. Is the second most modal auxiliary verb used. It accounts for 13.9% of all the modal verbs in the data. These modal verbs help you every day in your conversation.
It is important to learn their correct usage. To improve your English communication skills, you can join a course and learn grammar in-depth. A spoken English course will not only help you develop your English communication skills but also will make you fluent in the language. These helping verbs are can, could, will, would, shall, should, may, might, must, ought to, have to, has to and had to.
These are also known as modal auxiliaries. They express the degree of certainty of the action in the sentence or the attitude or opinion of the writer/speaker concerning the action. Modal verbs are a fundamental part of English because they express obligations, abilities, probabilities, suggestions and much more. So learning how to use modal verbs can really improve your level of fluency.
Let's have a look to see what modal verbs have in common and the many ways they can be used. There are ten common modal auxiliary verbs and they are 'can', 'could', 'will', 'would', 'shall', 'should', 'may', 'might', 'must' and 'ought'. Studied the use of modal auxiliary verbs in Horoscope. When the modal verbs 'should' or 'ought to' are used it indicates that there is a requirement to carry out an action, but it has yet been completed.
There could be many reasons why that obligation has not been enacted. Usually, a phrase, clause or sentence will explain why the action has not yet been completed. The connective 'but' often links the clauses. With modal verbs, use the infinitive form of the main verb without "to". Verbs that show degrees of necessity and certainty.
One common situation where modals are used is in classroom rules. In these rules, the underlined modal verbs show degrees of necessity. Modal verbs indicate possibility, obligation or ability. Find out how your child will be taught about modal verbs in grammar lessons in KS2 and the kinds of activities they might be asked to complete in the primary-school classroom. We often use modal verbs or other modal expressions when we want to express an opinion or attitude about a possible fact or to control a possible action.
All modal expressions are about the speaker's or writer's view of the world. The nine main modal verbs express a range of meanings, which may differ very subtly. The main meanings, especially those used in formal English, will be summarised here. English Modal Verbs of Obligation The main verbs of obligation are; MUST, HAVE TO, SHOULD. The past of have to / has to is had.
A modal verb is a special type of verb. Modal verbs change or affect other verbs in a sentence. They are used to show the level of possibility, indicate ability, show obligation or give permission.
Modal verbs behave differently to 'ordinary' verbs. Modal verbs add meaning to the main verb in a sentence by expressing possibility, ability, permission, or obligation. The main verbs of obligation are; MUST, HAVE TO, SHOULD. The past of have to / has to is had. Part 1 explains the grammar of modal verbs and where they are placed in a sentence or question. Part 2 explains the meaning of each modal verb and provides example sentences. Modals are a type ofauxiliary verb – they work with other verbs to express a range of different meanings.